Thyroxine and Triiodothyronine - Iodine Containing Thyroid Hormones
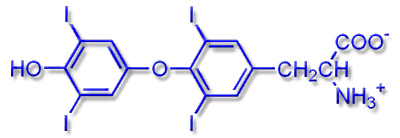
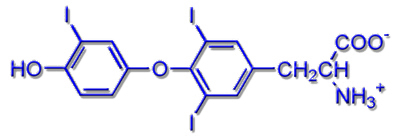
The iodine containing hormones tetraiodothyronine (thyroxine or T4) and triiodothyronine are structurally nearly equivalent. The only difference is the fourth iodine substituent in thyroxine. This difference leads to different bond strengths between the hormones and receptor molecules, which can be used for selective transport.
The tetrameric protein transthyretin has two binding sites for tetraiodothryonine. In mammals, this transport protein is responsible for most of the transport of thyroxine from blood serum to the brain, but it has virtually no affinity for triiodothyronine.
Schematic depiction of tetraiodothyronine (thyroxine) |
3D-Depiction of transthyretin with docked thyroxine molecules |
|
|
|
Schematic depiction of triiodothyronine |
|
|