"Classical" Copper Centers in Proteins
Copper participates in many biological processes involving electron transfer reactions. Its roles are as widely varied as simple electron transfer, oxygen activation, and oxygen transport.
In this sense, the copper proteins often have functions which can be carried out by iron centers. This is an indication that natural evolution was "success-oriented" and not "structure-oriented." A good example of this is the enzyme nitrite reductase. Its active site can be either an iron haem center or a type I copper complex.
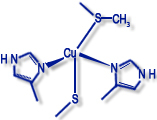
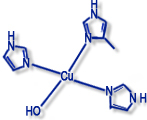
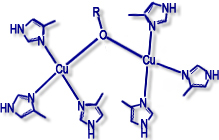
Copper proteins are often classified as type I, type II, or type III centers, depending on the environment of the metal ion and spectroscopic characteristics (EPR spectrum, color, etc).
Type I ("blue" copper proteins) |
Type II ("non-blue" copper proteins) |
Type III (dimers) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Examples: plastocyanin, azurin, nitrite reductase |
Examples: galactose oxidase, amine oxidase, dopamine monooxidase |
Examples: haemocyanin, tyrosinase |